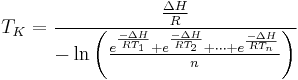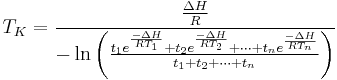Mean kinetic temperature
Mean kinetic temperature (MKT) is a simplified way of expressing the overall effect of temperature fluctuations during storage or transit of perishable goods. The MKT is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
The mean kinetic temperature can be expressed as:
Where:
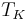 is the mean kinetic temperature in kelvins
is the mean kinetic temperature in kelvins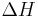 is the activation energy (typically within 60–100 kJ·mol-1 for solids or liquids)
is the activation energy (typically within 60–100 kJ·mol-1 for solids or liquids)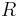 is the gas constant
is the gas constant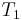 to
to 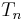 are the temperatures at each of the sample points in kelvins
are the temperatures at each of the sample points in kelvins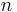 is the number of temperature sample points
is the number of temperature sample points
The above equation is valid only when the temperature readings are taken at the same interval. A more general form for the above equation can be expressed as:
Where:
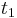 to
to 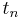 are time intervals at each of the sample points
are time intervals at each of the sample points
When 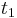 =
=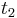 =
= =
=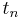 , this equation will be reduced to the former equation.
, this equation will be reduced to the former equation.